Table of Contents
According to Global Footprint Network, the world’s carbon footprint has increased by 700% since 1961. Thus, understanding the carbon footprint of our actions is crucial for implementing strategies and minimizing it as much as possible, and it begins with each person’s daily choices.
01
of 04
What is a carbon footprint?
A carbon footprint, which is measured in tons of CO2 emissions, is the total amount of greenhouse gases (GHGs), specifically carbon dioxide (CO2) and other carbon compounds such as methane (CH4), nitrogen oxide (N2O), hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs), perfluorocarbons (PFCs) and sulphur hexafluoride (SF6), released into the atmosphere as a result of everyday economic and human activities – either directly or indirectly.
These gases create a layer and “trap” the heat in the Earth’s atmosphere, contributing to global warming and climate change.
Greenhouse gases are released through various human activities such as transportation, industrial processes, agriculture, and deforestation but also through the simplest activities such as turning on the lights or cooking if you get your energy from a supplier that doesn’t use renewable sources. The same applies to your groceries. For example: if you buy from local producers, you’ll probably be able to reduce your carbon footprint since that food did not travel from the other side of the globe.
So it’s clear that the carbon footprint doesn’t only apply to human beings. Companies’ activities play a huge part in this process, too, especially during manufacturing, transport, and energy consumption—and this is an increasingly important concern for consumers when making a choice.
In fact, according to The Pandemic is Heightening Environmental Awareness study, 87% of consumers believe companies should integrate environmental concerns more fully into their products, services, and operations than they have in the past.
02
of 04
Carbon credits
The trading of carbon credits began in 1997 with the Kyoto Protocol, the first international agreement to reduce greenhouse gas emissions. It is a mechanism to help countries and companies meet their emission reduction targets.
These credits are certificates regulated by the United Nations and represent a ton of carbon that has been avoided.
But how do the credits work?
- In a cap-and-trade system, a government sets a ceiling on the total amount of greenhouse gases that certain industries or sectors can emit, so they are allocated a certain number of carbon credits, which represent their permitted emissions.
- Companies that emit fewer greenhouse gases than their allocated credits can sell their excess credits to other companies that exceed their limits. This creates a market for carbon credits, where the price is determined by supply and demand.
- Carbon credits can also be generated through projects that reduce or remove greenhouse gas emissions, such as reforestation. These projects are certified by independent organizations, and the credits they generate can be sold to companies or individuals looking to offset their emissions.
To put it simply, companies with a high level of GHG emissions can buy credits from other, more sustainable organizations, thus offsetting their emissions. Overall, carbon credits provide an economic incentive for companies to reduce their emissions and invest in cleaner technologies while also funding emissions reduction projects worldwide.
In this context, sustainability goes beyond mere compliance with environmental regulations; it reflects a strategic and ethical approach to business operations. By actively participating in carbon credit programs, companies demonstrate their dedication to minimizing their environmental impact and contributing to the broader sustainability goals.
Take Salesforce‘s example – they have been working on sustainability initiatives for some time, and their specific commitment to achieving net zero emissions by 2050 was announced in September 2017. This announcement marked a significant step in their sustainability journey, which includes reducing their emissions and collaborating with customers and partners (like us!) to achieve a broader goal.
Salesforce emphasizes a strong focus on environmental responsibility as part of their corporate culture. We can identify specific milestones like the launch of the Sustainability Cloud (now Net Zero Cloud) in 2019, which aimed to help businesses track and manage their environmental impact.
03
of 04
The Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD)
Building on Salesforce’s existing commitment to sustainability, which included achieving net zero emissions by 2050 and launching Net Zero Cloud in 2019, Salesforce’s efforts dovetailed nicely with the growing global focus on corporate environmental responsibility.
One case of this growing concern is the Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD), a law that requires companies to publish their sustainability efforts. By requiring businesses to disclose their social and environmental impact, the CSRD aims to increase their public accountability.
The Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive, whose plans the European Union finalised in late 2022, will come into effect in 2024.
-
From 1 January 2024, companies already subject to the non-financial reporting directive will need to start reporting for 2025
-
From 1 January 2025, all large companies meeting the criteria explained above will need to report for 2026
-
From 1 January 2026, all listed SMEs will need to report for 2027. However, SMEs can opt-out until 2028.
The sooner a company plans to meet the CSRD, the easier reporting will be. But how will you start?
As we delve deeper into sustainable practices, Salesforce’s Net Zero emerges as a key player. The introduction of Net Zero Cloud, Salesforce’s cloud-based sustainability solution, marks a significant stride toward actionable environmental impact and can be the solution you need to adhere to the CSRD.
In our next chapter, we will explore how Salesforce facilitates the measurement of carbon footprints—a crucial step towards realizing a more sustainable future.
04
of 04
Get to know Salesforce’s Net Zero Cloud
Calculating and reducing our carbon footprint is essential for mitigating climate change and transitioning to a more sustainable way of living. This involves efforts to decrease energy consumption, transition to renewable energy sources, improve energy efficiency, adopt eco-friendly transportation options, and implement sustainable practices in various sectors of the economy.
Based on this, and given that Salesforce has always been a pioneering organization when it comes to sustainability and social responsibility, in 2022 it reached the important milestone of being a “net zero carbon emission” company, a goal that all organizations face in the coming years.
To achieve this, Salesforce used its platform to manage its emissions and with this created the Net Zero Cloud platform, to make this process, which is time-consuming and complex, quicker and easier to help organizations manage their environmental impact and monitor their progress in reducing emissions towards the ultimate goal of being net zero.
Being their own first customer, Salesforce could understand the needs for this kind of project and so, build a tool that suits all companies’ requirements.
One of the major challenges with carbon accounting is the sheer volume of data. Salesforce Net Zero Cloud solves this problem with an AI tool called the Data Gap Filling that can catch inconsistencies and fix or estimate incorrect or missing data.
Also, many different gasses contribute to global warming, each one with its particularities, accordingly to their different scopes. But what’s the difference between the scopes?
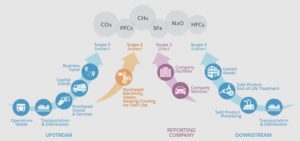
Scope 1 – direct impacts such as with buildings and company cars;
Scope 2 – indirectly and supplier dependent such as electricity and water;
Scope 3 – company activities such as business travels (as you can see in the example below), hotels, transportation, distribution, and purchased goods.
Source: Salesforce Trailhead – Track Emissions with Net Zero Cloud
That being said, what Salesforce do is group the emission factors by the scope they occupy and then define the calculations to be used. As these are quite complex, it is very useful to have them pre-filled in Net Zero Cloud.
One of the main features of the Net Zero Cloud with regard to carbon footprint is carbon footprint forecasting, which is used to design a forecasting model of your company’s scope 1, 2 and 3 emissions in order to set targets for the future and create sustainability commitment using a built-in module that complies with the Science Based Targets initiative (SBTi), which dictates the guidelines and tools that companies can use to set Net-Zero targets in line with science.
In essence, Net Zero Cloud is a group of objects collected together, and this way, it’s possible to track energy patterns and emission trends and evaluate environmental impact to give decision-makers the tools needed to formulate a climate action plan and begin to drive sustainability solutions.
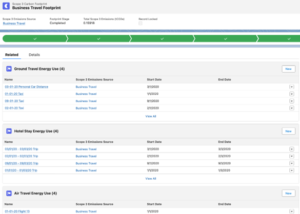
As an official Salesforce partner and implementation company, we can help you manage all ESG data in one place, communicating the company’s sustainability progress and engaging stakeholders. With our knowledge of Salesforce Reporting and Dashboards and our CRM Analytics expertise, we will configure Net Zero Cloud and use executive reporting dashboards to provide deeper insights and enable you to showcase your commitment.







